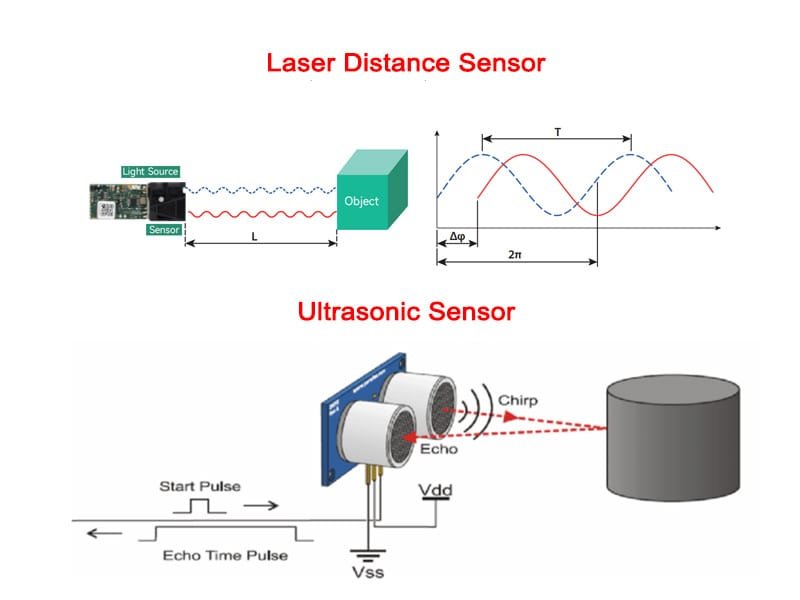
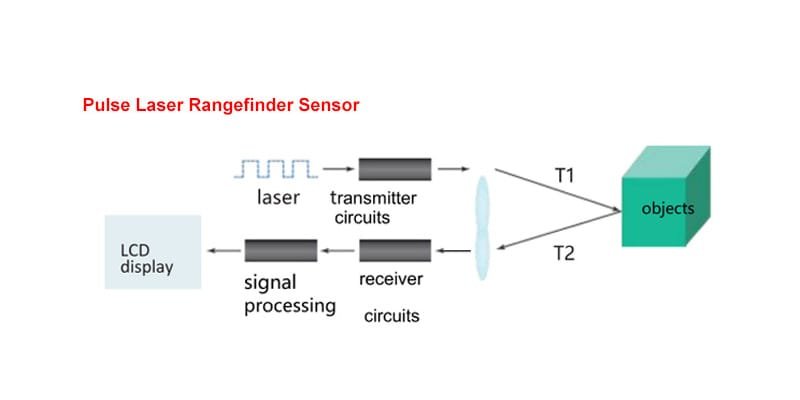
Complete Guide to LRF Module Divergence Angle — How to Choose the Right Beam Spread for Your Application
What Is Divergence Angle in an LRF Module?
The divergence angle of a Laser Rangefinder (LRF) module describes how much the laser beam spreads out as it travels over distance. It is typically measured in milliradians (mrad).
A smaller divergence angle produces a narrower beam over long distances, allowing precise targeting of small or distant objects. A larger divergence angle creates a wider beam, which may be more forgiving for moving or large targets but less precise for pinpoint measurements.
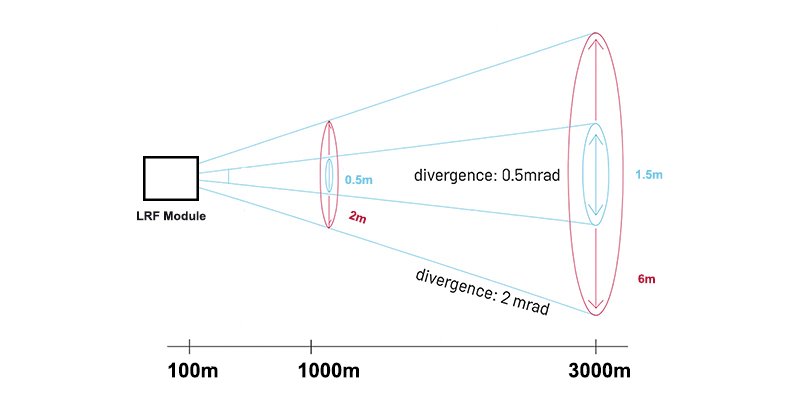
How to Calculate Divergence Angle
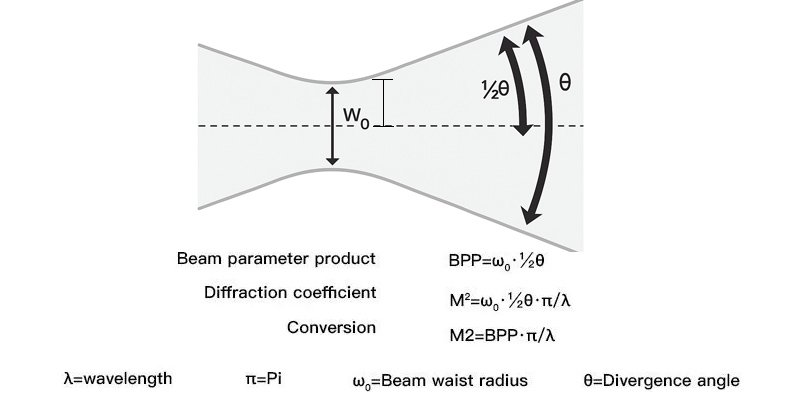
Divergence angle can be estimated using the formula:
Beam Diameter at Distance = Initial Beam Diameter + (Divergence × Distance)
For example:
- If a LRF Module has a divergence of 1 mrad, the beam will expand by 1 meter for every 1,000 meters traveled.
- At 3 km, that beam would be 6 meters wider than at the origin.
Why Divergence Angle Matters
The divergence angle affects several key aspects:
- Measurement Accuracy – Narrow beams allow precise detection of small targets.
- Signal Strength – Less divergence means more concentrated energy reaching the target.
- Environmental Performance – Lower divergence improves performance in fog, rain, or dust.
- Target Recognition – Wider beams may capture more background noise, affecting accuracy.
Recommended Divergence Angles by Application
- Long-Range Precision (Surveying, Military Targeting) → 0.3–0.8 mrad
- Medium-Range with Moderate Accuracy (Industrial Automation, Vehicle Detection) → 1–2 mrad
- Short-Range Wide Coverage (Object Scanning, Collision Avoidance) → 2–5 mrad
How to Choose the Right Divergence Angle
- Consider Your Target Size – Small targets require a tighter beam.
- Consider Your Operating Distance – Long distances benefit from low divergence.
- Consider Environmental Conditions – Low divergence performs better in challenging conditions.
- Balance with Detector Sensitivity – Ensure your sensor can detect the beam at the chosen divergence.
Conclusion

Understanding divergence angle is essential for choosing the right LRF module for your application. Whether you need pinpoint accuracy or broad coverage, selecting the proper beam spread will maximize measurement performance.