Introducing: Laser Distance Sensor Working Principle
Introduction: Laser distance sensors have revolutionized the way industries measure distances. Their ability to provide accurate and fast measurements has made them indispensable across fields like manufacturing, automation, and robotics. But what exactly is the Laser Distance Sensor working principle behind these powerful tools? In this article, we’ll explore the core technology that drives laser distance sensors and why they stand out compared to traditional measurement methods.

The Science Behind Laser Distance Sensors
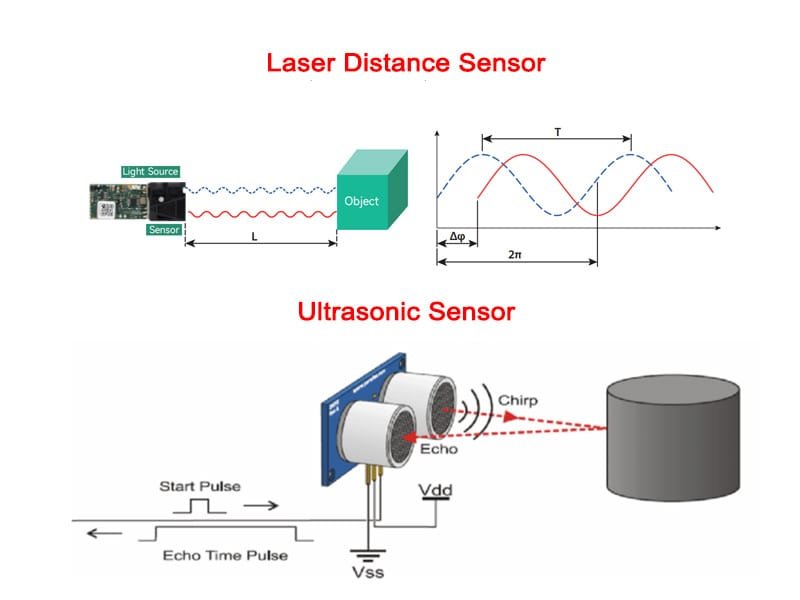
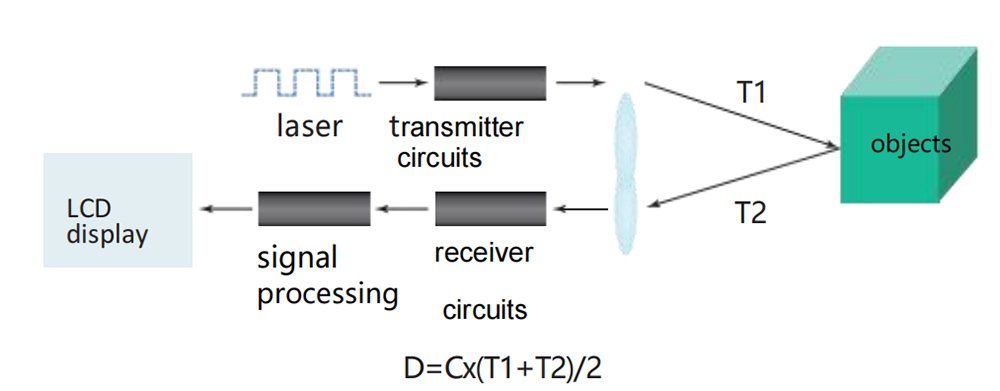
Laser distance sensors function based on the time-of-flight (ToF) principle. This method involves sending out a laser beam towards a target object and then measuring the time it takes for the light to return after hitting the object. The sensor’s processor then uses this time to calculate the distance, given the known speed of light.
Key Steps in the Process:
Emission: A laser diode emits a narrow, focused beam of light.
Reflection: The light travels to the object and reflects back to the sensor.
Measurement: The sensor measures the time between emission and reflection.
Calculation: Using the formula
Distance=Speed of Light×Time/2, the sensor calculates the distance.
Different Types of Laser Distance Sensors
Not all laser distance sensors use the same technology. Here are the main types:
Time-of-Flight (ToF) Sensors: These measure the time taken for the light to return to the sensor.
Phase-Shift Sensors: These sensors compare the phase shift between the emitted and returned light waves to calculate distance.
Triangulation Sensors: For shorter distances, the sensor measures the angle of the reflected laser to determine how far the object is.
Each type has its unique advantages depending on the application, whether you’re measuring long distances in industrial automation or short-range precision measurements in robotics.
Why Use Laser Distance Sensors?
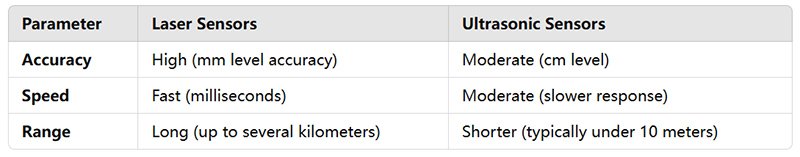
High Precision: Laser distance sensors provide measurements down to the millimeter, making them ideal for applications requiring extreme accuracy.
Fast Response Time: The speed of laser sensors makes them perfect for dynamic environments where rapid measurements are crucial, such as in automated production lines.
Non-Contact Measurement: As they don’t require physical contact with the target, laser distance sensors can measure difficult-to-reach or hazardous areas safely and efficiently.
Long Range: Depending on the type, these sensors can measure distances from a few centimeters up to several hundred meters.
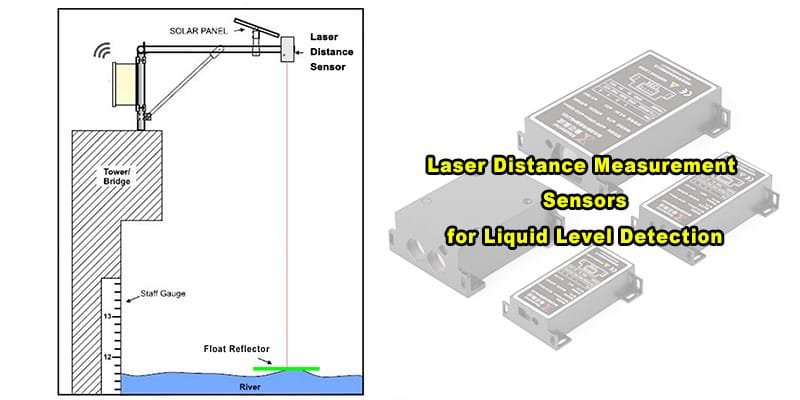
Applications of high-precision Laser Sensors
Laser distance sensors are used in a wide range of industries:
Manufacturing: For quality control, part measurement, and monitoring during production.
Construction: In surveying and building layout for accurate measurements over long distances.
Robotics: Used in navigation systems, laser distance sensors allow robots to sense their surroundings and navigate autonomously.
Whether you’re involved in robotic automation or construction layout, understanding the core working principle helps you choose the best sensor for your needs.

Challenges and Limitations of Laser Distance Sensors
Although laser distance sensors offer many advantages, they are not without challenges:
Surface Reflection Issues: Highly reflective or transparent surfaces can affect the sensor’s ability to get an accurate reading.
Environmental Conditions: Excessive dust, smoke, or ambient light can interfere with the laser’s accuracy.
Cost: High-precision laser sensors can be more expensive than other types of distance measurement tools, such as ultrasonic sensors.
How to Choose the Right high-precision Laser Sensors
When selecting a laser distance sensor for your application, consider the following:
Range Requirements: For long-distance applications, a Time-of-Flight sensor is often the best choice.
Surface Type: If you’re measuring glossy or transparent surfaces, look for sensors that are equipped to handle challenging materials.
Environmental Conditions: If the sensor will be exposed to dust, moisture, or bright light, ensure it has protective features or consider alternative methods.
Conclusion
Understanding the Laser Distance Sensor Working Principle highlights their incredible utility in a variety of industries. By emitting and reflecting light, these sensors provide accurate, fast, and non-contact measurements across a wide range of distances. Whether in manufacturing, construction, or robotics, laser distance sensors are an invaluable tool for anyone needing precise distance measurement.