Laser vs Ultrasonic Distance Sensor: Which Is Right for Your Application?
Introduction: Distance sensors play a crucial role in automation, manufacturing, and many other industries. Among the most popular are laser and ultrasonic distance sensors. Both technologies serve similar purposes but operate on different principles, each with its advantages and limitations. In this article, we will compare laser and ultrasonic distance sensors to help you determine which is best suited for your needs.
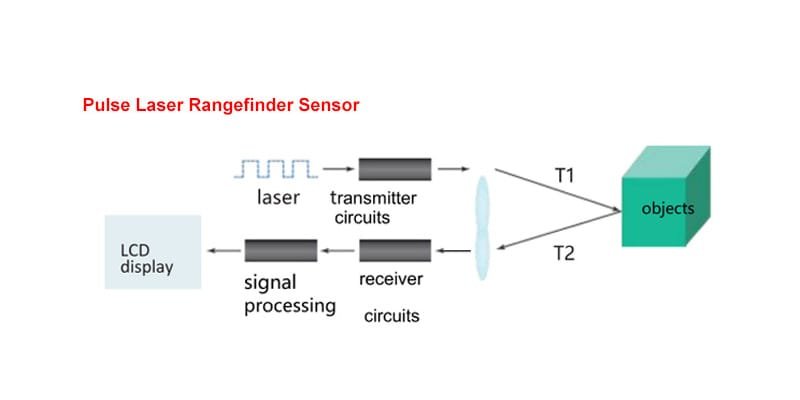
How Do Laser Distance Sensors Work?
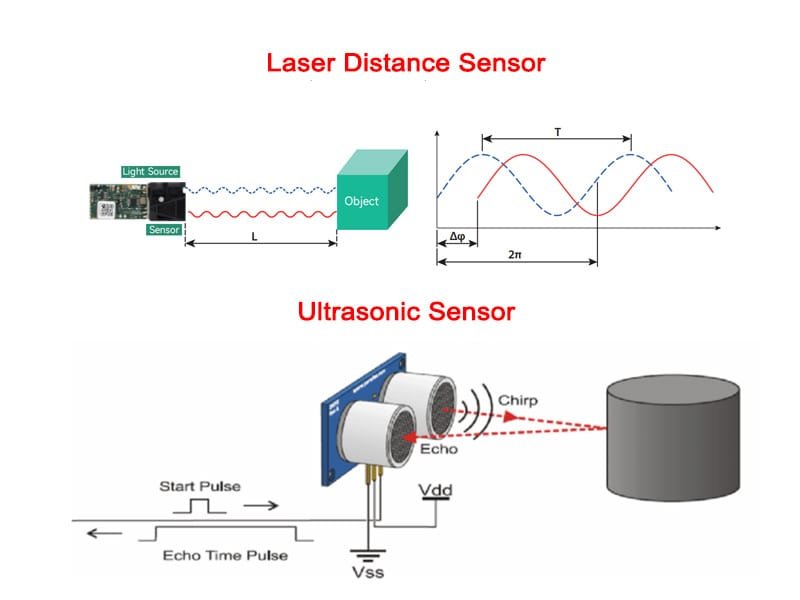
Laser distance sensors operate using a focused beam of light to measure distance. They emit a laser that reflects off the target object, and the sensor calculates the distance based on the time it takes for the light to return (time-of-flight principle). This makes them highly accurate and fast.
Advantages:
High Accuracy: Lasers can measure with millimeter precision.
Long Range: Some laser sensors can measure distances over 100 meters.
Fast Measurement: Instant results, ideal for high-speed applications.
How Do Ultrasonic Distance Sensors Work?
Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to measure distances. They emit high-frequency sound waves that bounce off the target, and the sensor calculates the distance based on the time it takes for the sound to return. This makes ultrasonic sensors particularly useful for objects that are non-reflective or have uneven surfaces.
Advantages:
Non-Reflective Surface Capability: Works on a variety of materials, including those that don’t reflect light well.
Cost-Effective: Generally more affordable than laser sensors.
Environmentally Resistant: Less affected by dust, moisture, or lighting conditions.
Key Differences Between Laser and Ultrasonic Distance Sensors
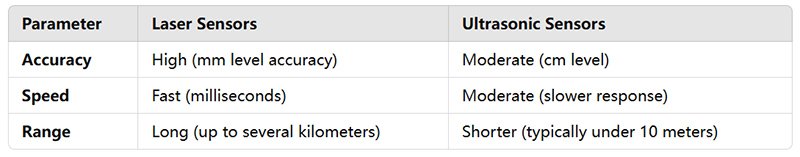
Accuracy:
Laser sensors offer far greater precision, making them ideal for applications where millimeter accuracy is critical, such as in manufacturing quality control.
Ultrasonic sensors, while less accurate, are sufficient for broader measurements, especially in outdoor settings where precision isn’t as crucial.
Range:
Laser distance sensors can measure much longer distances, up to hundreds of meters, making them suitable for industrial automation.
Ultrasonic sensors typically have a shorter range, maxing out around 10-20 meters.
Surface Compatibility:
Laser sensors can struggle with dark, glossy, or reflective surfaces due to irregular light reflection.
Ultrasonic sensors perform better on complex surfaces, such as liquids, fabrics, or irregular objects.
Environmental Factors:
Laser sensors can be disrupted by lighting conditions or airborne particles.
Ultrasonic sensors perform well in environments with dust, moisture, or low visibility.
Applications of Laser and Ultrasonic Sensors
Laser Distance Sensors:
Manufacturing: For high-precision part measurements and automation.
Surveying: Long-range distance measurements in construction and land surveying.
Robotics: Used for guiding autonomous systems with high precision.
Ultrasonic Distance Sensors:
Parking Sensors: Commonly used in vehicles for obstacle detection.
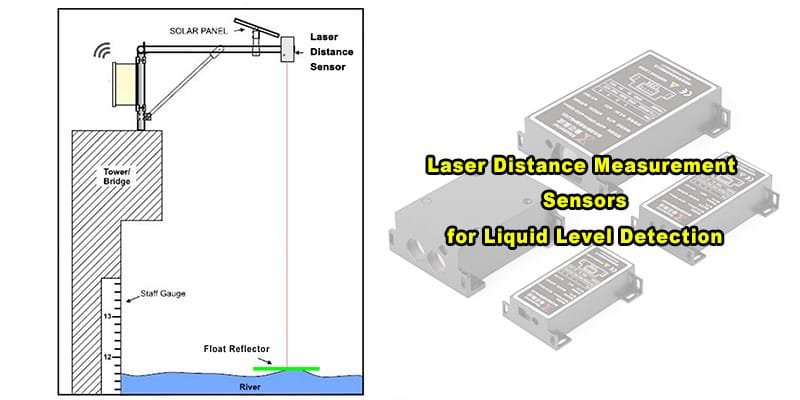
Level Measurement: Monitoring liquid levels in tanks.
Agriculture: Ideal for use in environments with dust and moisture.
Which One Should You Choose?
The decision between a laser and ultrasonic distance sensor depends on your specific application. If your priority is precision over long distances or measuring reflective surfaces, a laser distance sensor is your best option. However, if you’re working in harsh environments or need to measure complex, non-reflective surfaces, an ultrasonic sensor might be more appropriate.
Conclusion:
Both laser and ultrasonic sensors have their strengths and are suited for different applications. Understanding the differences can help you make an informed decision for your specific use case. Whether you’re working in manufacturing, robotics, or industrial automation, selecting the right sensor can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy.