Temassız Mesafe Ölçüm Sensörleri Modern Otomasyonda Neden Önemli Hale Geliyor?
As global industries accelerate toward digitalization and autonomy, the demand for highly reliable, fast, and precise measurement technologies continues to grow. Among these innovations, the temassız mesafe ölçüm sensörü has become one of the most essential components powering automation, robotics, and intelligent machinery. Its ability to measure distance without physical interaction makes it ideal for environments where precision, safety, and durability are paramount.
Today, manufacturers, system integrators, and robotics developers increasingly rely on this sensor technology to improve operational visibility, reduce mechanical wear, and enable faster decision-making in real time. This article explores the key reasons behind the rising adoption of non contact measurement technologies, how they advance automation capabilities, and why industries across the world are rapidly integrating them into next-generation systems.

1. Automation Requires Speed and Zero-Contact Measurement
Modern automated systems—from robotic arms to warehouse conveyors—can no longer depend on physical switches or contact-based measurement tools. Mechanical sensors slow devices down due to friction and require frequent replacement.
Bu temassız mesafe ölçüm sensörü eliminates the need for physical interaction, enabling continuous, high-speed measurement. Because there is no mechanical wear, these sensors dramatically improve machine uptime, reduce failure rates, and ensure consistent data output across long operating cycles.

In fast-moving production lines, even a 50 ms delay can affect final yield. With high-precision laser-based technology, many sensors now deliver measurements at dozens or even hundreds of hertz, meeting the demand for real-time automation.
2. Precise Distance Measurement Is Critical for Robotics
Robots, whether industrial or mobile, depend heavily on spatial perception. Navigation, object detection, gripping, alignment, and positioning all require highly accurate distance data.
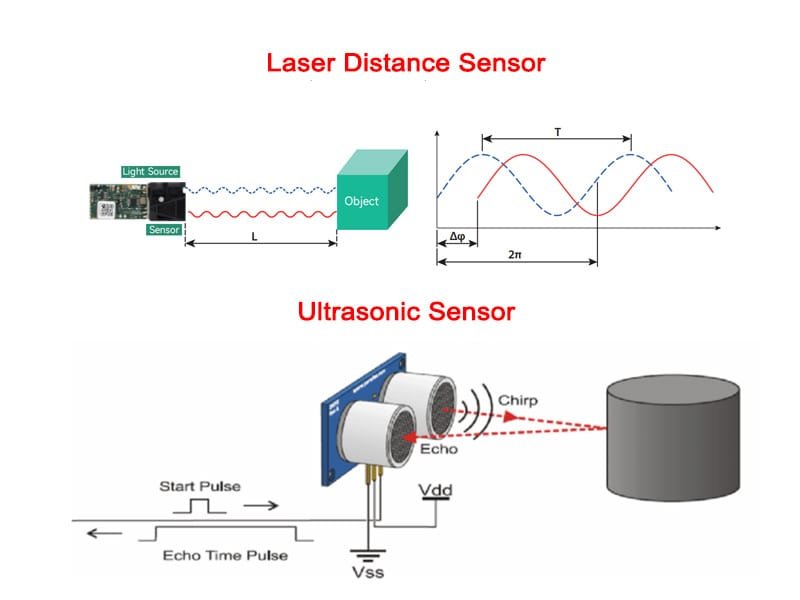
This is where the temassız mesafe ölçüm sensörü excels. Unlike ultrasonic or infrared sensors, laser-based solutions offer millimeter-level accuracy and stable performance across variable lighting conditions.
The long-tail keyword non contact sensor for robotics has become increasingly relevant, especially with the rise of AGV and AMR systems used in logistics and manufacturing. As autonomous robots navigate complex environments, precise distance feedback ensures collision avoidance, smooth path planning, and reliable docking.
3. High Precision for Industrial Manufacturing
Industrial automation requires measurement accuracy that traditional sensors cannot provide. Machining tolerance, quality inspection, PCB alignment, and semiconductor processes all depend on high-resolution distance measurement.
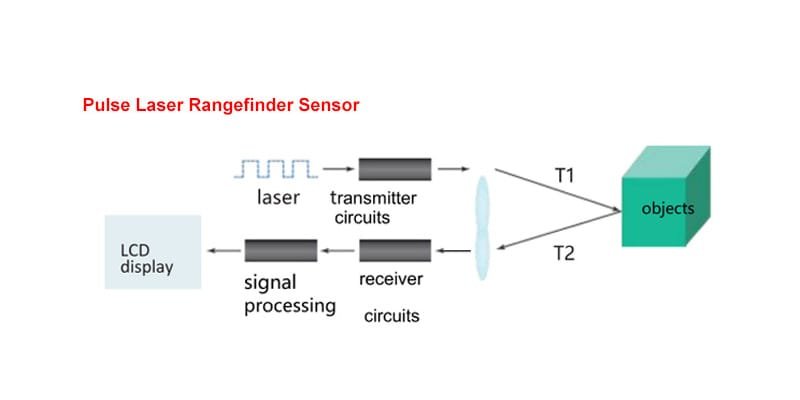
With technologies such as phase-shift measurement and time-of-flight laser sensing, the modern yüksek hassasiyetli lazer mesafe sensörü provides consistent results even on challenging surfaces such as glossy metal, black plastic, or rough materials.
Laser-based non contact measurement also reduces uncertainty caused by vibration or rapid motion. This stability is crucial in industries like automotive manufacturing, semiconductor packaging, and smart logistics systems that rely on micron-to-millimeter precision.

4. Durability in Harsh or Sensitive Environments
Non contact sensing removes the risk of contamination, deformation, or interference in applications where physical contact is not possible or not safe. Environments such as:
- High-temperature equipment
- Chemical production
- High-pressure systems
- Clean rooms
- Electronics manufacturing
- Food and medical processing
all benefit from a temassız mesafe ölçüm sensörü that does not degrade with use. Since the measuring element never touches the target, the sensor remains stable even in dusty, vibrating, or corrosive conditions.
This longevity significantly reduces maintenance costs and enhances system reliability—two major priorities for modern automation users.
5. Integration with Smart Manufacturing and IoT
As factories evolve toward Industry 4.0, smart measurement devices must integrate seamlessly into digital ecosystems. Today’s industrial non contact measurement sensor supports multiple protocols such as UART, RS485, Modbus, CAN, and MQTT through gateways.
This connectivity allows distance information to feed directly into:
- Cloud-based monitoring dashboards
- Predictive maintenance systems
- Digital twins
- AI-driven optimization algorithms
The shift from isolated equipment to fully connected smart factories makes high-accuracy distance feedback indispensable. Non contact measurement provides the clean, reliable data streams required for automation intelligence and data-driven decision making.
6. Growing Adoption Across Multiple Industries
The demand for automation distance measurement technology is expanding rapidly across sectors:
Robotics & AGV / AMR Systems
Ensures obstacle detection, precise docking, and navigation.
Warehouse and Logistics
Used for package dimensioning, pallet detection, and conveyor control.
Industrial Machinery
Supports alignment, positioning, and range monitoring in real time.
Akıllı Tarım
Helps measure plant spacing, vehicle height control, and UAV flight stabilization.
Smart Transportation & Traffic Systems
Used for vehicle detection, safety monitoring, and infrastructure automation.
The wide range of use cases proves the versatility of the automation distance measurement sensor, and explains why global demand is rising at double-digit growth rates.
Sonuç
The shift toward autonomous, efficient, and highly precise manufacturing has made the temassız mesafe ölçüm sensörü a foundational building block for modern automation. Its durability, accuracy, high speed, and broad integration capabilities allow companies to achieve better productivity, safer operations, and more intelligent workflows.
As industries continue upgrading toward digital, autonomous, and AI-enhanced systems, non contact measurement technology will only grow more essential—solidifying its place as one of the most influential tools in the next generation of industrial automation.