レーザー距離センサーとレーザー三角測量センサー:主な違いを説明
近距離測定センサーは、特にロボット工学、倉庫物流、半導体生産、スマート農業、高精度工場検査など、現代の産業オートメーションに不可欠なものである。この分野で最も広く使用されているセンシング技術は、次の2つである。 レーザー距離センサー そして レーザー三角測量センサー (光学式変位センサーとも呼ばれる)。.
一見したところ、どちらのセンサーも近距離探知に適しているように見える。しかし 動作原理、測定範囲、精度挙動、設置要件、環境耐性、アプリケーション適合性 は根本的に違う。.
この記事では、エンジニアがプロジェクトに最適なテクノロジーを判断できるよう、技術レベルとアプリケーションレベルの詳細な比較を行う。.
1.各センサーの働き
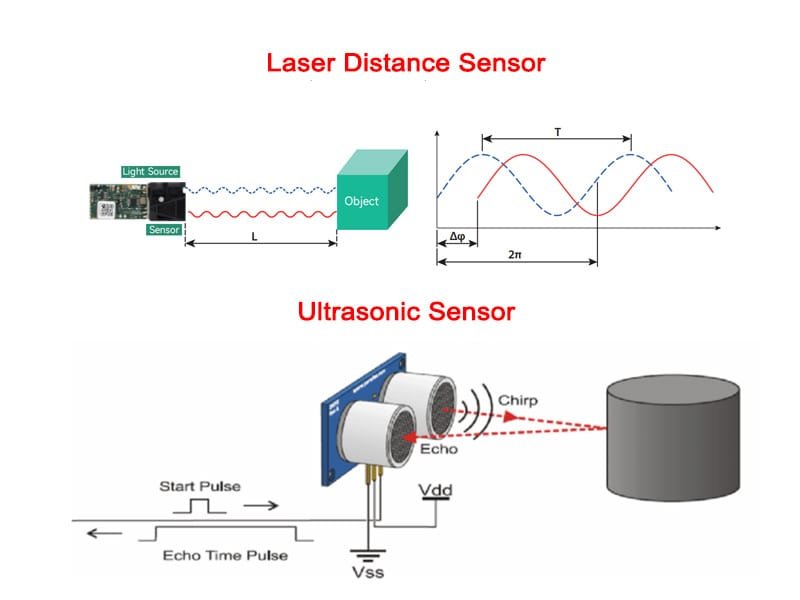
1.1 レーザー距離センサー(位相シフトまたはTOF測定)
A レーザー距離センサー 通常、距離測定には位相シフト測距または飛行時間(TOF)を使用する。.
動作原理:
- センサーは変調またはパルスレーザー光線を照射する。.
- 反射ビームはセンサーに戻る。.
- システムは位相差またはリターンタイムから距離を計算する。.
主な強み
- 距離計算はレンズ形状やビーム三角測量に依存しない
- 数メートルの距離でも高い精度
- 角度や対象物の色に関係なく安定した性能
- 優れた屋外安定性と耐ノイズ性
- 暗い、粗い、反射率の低いターゲットに効果的
これによって レーザー距離センサー 安定性と信頼性が重視される産業グレードのシナリオに最適です。.
1.2 レーザー三角測量センサー(光学幾何変位)
三角測量センサーは 幾何学に基づく光学原理.
動作原理:
- レーザースポットがターゲット表面に投影される。.
- 反射したスポットはレンズを経由してCMOS/CCD/PSDセンサーに当たる。.
- 距離が変わると、検出器上で光点が移動する。.
- センサーは変位角度に基づいて距離を計算する。.
主な強み
- 至近距離で極めて高い解像度
- マイクロメーターレベルの変位検出に最適
- 速い応答速度と高感度
制限:
- 表面の色、角度、反射率に強く影響される
- 測定範囲は通常短い(10~500mm)
- 屋外での使い勝手の悪さ
- 安定性の高い取り付け条件が必要
したがって、三角測量センサーは実験室や管理された製造環境に適している。.
2.測定範囲と性能の比較
| 特徴 | レーザー距離センサー | レーザー三角測量センサー |
|---|---|---|
| 典型的な範囲 | 0.03 m - 200 m | 10 mm - 500 mm |
| 暗い/黒いターゲットに使用可能 | はい | しばしば不安定 |
| 屋外パフォーマンス | 非常に強い | 非常に弱い |
| 角度公差 | 高い | 低い |
| レンジの柔軟性 | ワイド | 非常に狭い |
| マイクロレベルの精度 | ミディアム | 非常に高い |
について レーザー距離センサー 必要なレンジが0.5mを超える場合、あるいは環境に対する堅牢性が重要な場合は、常にこの方式が優位となる。.
3.精度、安定性、耐環境性
3.1 レーザー距離センサー
精度:通常 ±1mm
周波数:モデルにより最大30-100 Hz
メリット
- 屋内外での安定性
- 日光、ほこり、霧、弱い反射に強い
- 角度変化によるドリフトを最小限に抑える
- 金属、プラスチック、布地、木材などに対応。.
- 移動体に最適
そのため、次のような用途に最適です。 産業オートメーション、ロボット工学、AGVナビゲーション、包装機械、選別システム、安全検知。.
3.2 レーザー三角測量センサー
精度:至近距離(マイクロメーターレベル)では極めて高い
周波数:多くの場合1~2kHz、微妙な振動の検出に適している
制限:
- 設置時の振動に極めて敏感
- 光沢のある表面や黒い表面では、光点が歪みやすい。
- 強い環境光に対応できない
- 最大航続距離の制限
こんな人に最適
- 半導体検査
- 表面高さ測定
- 精密組立
- 研究室での変位試験
4.アプリケーションの適合性
レーザーレンジセンサー
- AGVとAMRのナビゲーションと衝突防止
- ロボットアームの位置決め
- 倉庫オートメーション/フォークリフト・センシング
- 材料レベル検出
- インテリジェント農業機械
- コンパクトなアウトドア用品
- 産業機械の距離フィードバック
その耐久性と測定範囲は、実際のエンジニアリングに理想的です。.
三角測量センサー
- 微小変位測定
- エレクトロニクス組立ライン
- 表面の平坦度と厚さの分析
- 小さな機械的な動きの検出
- クリーンな環境での高精度検査
三角測量は、超短距離の正確さでは他の追随を許さないが、実用性ではそうではない。.

5.まとめ:どちらを選ぶべきか?
あなたのプロジェクトが必要なら:
長距離短距離測定 (0.1-80 m)
屋外での安定性
暗黒物体検出
堅牢性と柔軟性
あなたのプロジェクトが必要なら:
サブミリ表面検査
超至近距離検出(500mm未満)
制御された照明と安定した取り付け
ほとんどの産業用アプリケーション(特にロボット工学、オートメーション、AGVシステム)。
その レーザー距離測定センサー は、優れた効率性、信頼性、長期性能を提供する。.