レーザー計測センサーの選択ガイドシリーズ:正確な距離測定のための正しいソリューションの選び方
A laser measuring sensor has become an essential component in modern industrial automation, robotics, smart logistics, and intelligent infrastructure. Compared with traditional contact or ultrasonic sensors, laser-based measurement offers higher precision, longer range, faster response, and greater flexibility. However, choosing the right laser measuring sensor is not always straightforward. Different applications require different levels of accuracy, measurement distance, environmental adaptability, and system integration.
This article, as part of the Laser Measuring Sensor Selection Guide Series, provides a comprehensive overview of how to evaluate and select a suitable laser measurement sensor based on real-world application needs.
1. Understanding What a Laser Measuring Sensor Is
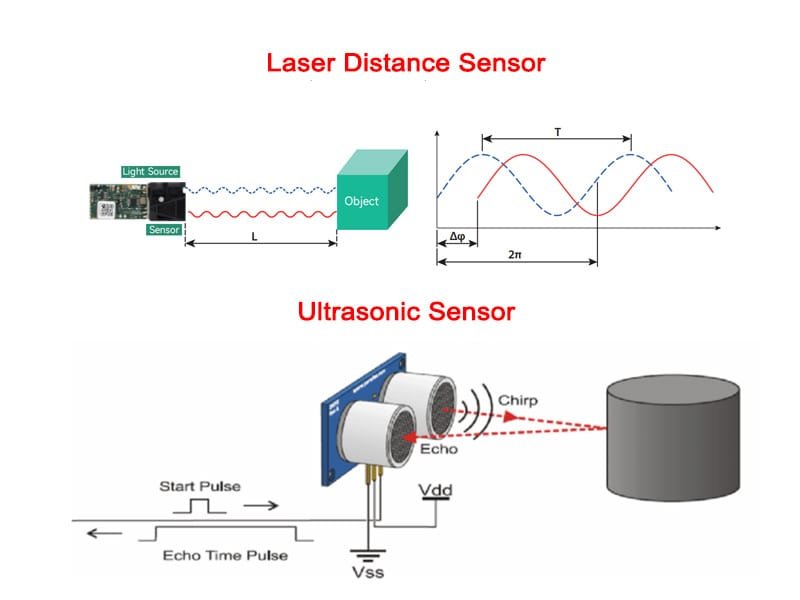
A laser measure sensor is a device that calculates distance by emitting a laser beam toward a target and analyzing the reflected signal. Depending on the working principle, common technologies include phase-shift measurement and time-of-flight (ToF).
For applications that demand micron- or millimeter-level precision, a レーザー距離測定センサー based on phase measurement is often preferred. For applications requiring long-range detection, such as outdoor monitoring or large-scale surveying, a レーザー距離計モジュール using pulse or ToF technology is typically more suitable.
Understanding these basic principles helps narrow down the sensor category before moving into more detailed specifications.

2. Measurement Accuracy: Define Your Precision Requirements
Accuracy is one of the most critical parameters when selecting a laser distance sensor. In industrial positioning, automated assembly, or precision inspection, even a small measurement error can cause system-level deviations.
A 高精度レーザー距離測定センサー can achieve accuracy levels of ±1 mm or better under stable conditions. These sensors are widely used in:
- Industrial automation and motion control
- Conveyor positioning systems
- Precision material handling
- Robotics and AGV navigation
However, higher accuracy often comes with stricter requirements for surface reflectivity, ambient light control, and installation stability. Therefore, selecting the highest accuracy available is not always the best choice—selecting accuracy that matches the actual application requirement is more cost-effective and reliable.
3. Measuring Range: Short, Medium, or Long Distance
The measuring range directly affects the choice of sensor technology. A laser distance sensor designed for short-range detection (below 10 m) may not perform well in outdoor or large-area environments.
A long distance measuring sensor is typically required for:
- Warehouse distance monitoring
- Smart traffic and infrastructure systems
- Outdoor level measurement
- Large equipment positioning
Long-range sensors often use pulse laser technology and may have lower accuracy than short-range phase-based sensors. In some applications, integrating a レーザー距離計モジュール into a custom system provides more flexibility in balancing range, accuracy, and system size.
4. Environmental Conditions: Indoor vs Outdoor Use
Environmental factors play a major role in sensor performance. Dust, fog, vibration, temperature variation, and strong ambient light can all affect measurement stability.
When selecting a laser measuring sensor, consider:
- Operating temperature range
- Resistance to dust and moisture (IP rating)
- Performance under strong sunlight
- Surface color and reflectivity of the target
For outdoor applications, a long distance measurement sensor with optimized optical filtering and stable signal processing is recommended. For indoor automation, a high accuracy laser distance measurement sensor often provides better consistency and repeatability.

5. Output Interface and System Integration
Modern laser distance sensors are rarely used as standalone devices. They must communicate seamlessly with controllers, PLCs, or embedded systems.
Common interfaces include:
- UART / TTL
- RS232 / RS485
- USB
- Modbus
- Analog output
For developers and system integrators, using a レーザー距離計センサー can simplify integration into custom hardware platforms such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or industrial controllers. Modules offer compact size, flexible communication options, and easier secondary development.
6. Size, Weight, and Power Consumption
In mobile platforms such as drones, robots, or portable equipment, size and power consumption become critical factors. A compact laser measuring sensor with low power consumption allows longer operating time and more flexible installation.
Laser rangefinder module designs are especially suitable for applications where space is limited, while still delivering stable distance measurement performance.
7. Application-Oriented Selection Strategy
Instead of focusing on a single parameter, the most effective way to choose a laser measuring sensor is to start from the application scenario:
- 産業オートメーション: prioritize accuracy, repeatability, and stable output
- 物流・倉庫: balance range, speed, and reliability
- Outdoor monitoring: emphasize long distance capability and environmental resistance
- Embedded systems: choose compact laser rangefinder modules with flexible interfaces
By aligning technical specifications with application demands, users can avoid over-specification and reduce overall system cost.

結論
Selecting the right laser measuring sensor requires a comprehensive evaluation of accuracy, measuring range, environment, integration requirements, and physical constraints. Whether you need a high accuracy laser distance measurement sensor for precision automation or a long distance measuring sensor for outdoor applications, understanding these key factors ensures reliable and efficient system performance.
As laser technology continues to evolve, laser measuring sensors and laser rangefinder modules will play an increasingly important role in intelligent sensing and automation systems across industries.