Sensor láser de alcance vs Sensor láser de triangulación: Explicación de las principales diferencias
Los sensores de medición de corta distancia son esenciales para la automatización industrial moderna, especialmente en robótica, logística de almacenes, producción de semiconductores, agricultura inteligente e inspección de fábricas de alta precisión. Dos de las tecnologías de detección más utilizadas en este campo son los sensor láser de alcance y el sensor de triangulación láser (también conocido como sensor óptico de desplazamiento).
A primera vista, ambos sensores parecen adecuados para la detección a corta distancia. Sin embargo, su principios de funcionamiento, rango de medición, comportamiento de la precisión, requisitos de instalación, tolerancia ambiental e idoneidad de la aplicación son fundamentalmente diferentes.
Este artículo ofrece una comparación detallada a nivel técnico y de aplicación para ayudar a los ingenieros a determinar qué tecnología es la más adecuada para su proyecto.
1. Funcionamiento de cada sensor
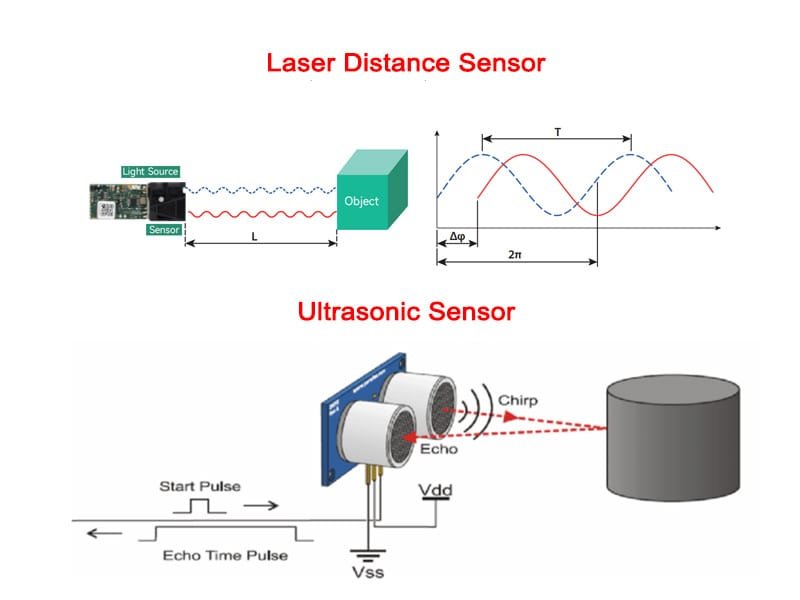
1.1 Sensor láser de alcance (desplazamiento de fase o medición TOF)
A sensor láser de alcance suele utilizar el desplazamiento de fase o el tiempo de vuelo (TOF) para medir la distancia.
Principio de funcionamiento:
- El sensor emite un haz láser modulado o pulsado.
- El haz reflejado vuelve al sensor.
- El sistema calcula la distancia a partir de la diferencia de fase o del tiempo de retorno.
Puntos fuertes:
- El cálculo de la distancia no depende de la geometría de la lente ni de la triangulación del haz
- Gran precisión incluso a varios metros
- Rendimiento constante independientemente del ángulo o el color del objeto
- Excelente estabilidad en exteriores y resistencia al ruido
- Funciona bien con objetivos oscuros, rugosos o poco reflectantes
Esto hace que el sensor láser de alcance ideal para situaciones industriales en las que la estabilidad y la fiabilidad son importantes.
1.2 Sensor láser de triangulación (desplazamiento geométrico óptico)
Un sensor de triangulación utiliza un principio óptico basado en la geometría.
Principio de funcionamiento:
- Se proyecta un punto láser sobre la superficie objetivo.
- El punto reflejado incide en un sensor CMOS/CCD/PSD a través de una lente.
- Al cambiar la distancia, el punto luminoso se desplaza en el detector.
- El sensor calcula la distancia en función del ángulo de desplazamiento.
Puntos fuertes:
- Resolución extremadamente alta a distancias muy cortas
- Excelente para detectar desplazamientos micrométricos
- Rápida velocidad de respuesta y alta sensibilidad
Limitaciones:
- Se ve muy afectado por el color, el ángulo y la reflectividad de la superficie
- Rango de medición típicamente corto (10-500 mm)
- Poca usabilidad en exteriores
- Requiere condiciones de montaje muy estables
Por ello, los sensores de triangulación son más adecuados para laboratorios y entornos de fabricación controlados.
2. Rango de medición y comparación de prestaciones
| Característica | Sensor láser de alcance | Sensor láser de triangulación |
|---|---|---|
| Alcance típico | 0,03 m - 200 m | 10 mm - 500 mm |
| Utilizable en objetivos oscuros/negros | Sí | A menudo inestable |
| Rendimiento al aire libre | Muy fuerte | Muy débil |
| Tolerancia angular | Alta | Bajo |
| Flexibilidad de la gama | Ancho | Muy estrecho |
| Precisión a micronivel | Medio | Extremadamente alto |
En sensor láser de alcance predomina cuando el alcance requerido es superior a 0,5 m o cuando la robustez ambiental es importante.
3. Precisión, estabilidad y resistencia ambiental
3.1 sensor láser de alcance
Precisión: normalmente ±1 mm
Frecuencia: hasta 30-100 Hz según el modelo
Ventajas:
- Estable en interiores y exteriores
- Resistente a la luz solar, el polvo, la niebla y los reflejos débiles
- Deriva mínima debida a los cambios de ángulo
- Funciona en metales, plásticos, tejidos, madera, etc.
- Ideal para objetos en movimiento
Esto la convierte en la mejor opción para automatización industrial, robótica, navegación AGV, máquinas de embalaje, sistemas de clasificación y detección de seguridad.
3.2 Sensor láser de triangulación
Precisión: extremadamente alta a corta distancia (nivel micrométrico)
Frecuencia: a menudo 1-2 kHz, buena para la detección de vibraciones sutiles
Limitaciones:
- Extremadamente sensible a las vibraciones de la instalación
- El punto de luz se distorsiona fácilmente en superficies brillantes/negras
- No soporta la luz ambiente intensa
- Alcance máximo limitado
El más adecuado para:
- Inspección de semiconductores
- Medición de la altura de la superficie
- Montaje de precisión
- Pruebas de desplazamiento en laboratorio
4. Idoneidad de la aplicación
sensor láser de alcance - Mejor para:
- Navegación AGV y AMR y anticolisión
- Posicionamiento del brazo robótico
- Automatización de almacenes / detección de carretillas elevadoras
- Detección del nivel de material
- Maquinaria agrícola inteligente
- Equipamiento compacto para exteriores
- Información a distancia para máquinas industriales
Su durabilidad y rango de medición lo hacen ideal para la ingeniería del mundo real.
Sensor de triangulación - Ideal para:
- Medición de microdesplazamientos
- Líneas de montaje de componentes electrónicos
- Análisis de planitud y espesor de superficies
- Detección de pequeños movimientos mecánicos
- Inspección de alta precisión en entornos limpios
La triangulación no tiene rival en cuanto a precisión de alcance ultracorto, pero no en cuanto a practicidad.

5. Resumen: ¿Cuál elegir?
Si su proyecto lo requiere:
Medición de corto alcance (0,1-80 m)
Estabilidad en el exterior
Detección de objetos oscuros
Robustez y flexibilidad
Si su proyecto lo requiere:
Inspección submilimétrica de superficies
Detección a muy corta distancia (<500 mm)
Iluminación controlada y montaje estable
En la mayoría de las aplicaciones industriales, especialmente en robótica, automatización y sistemas AGV.
el sensor láser de medición de distancias ofrece una eficiencia, fiabilidad y rendimiento a largo plazo superiores.