How to Optimize Robot Positioning and Obstacle Detection with Laser Measurement Sensor
Introduction
With the rapid advancement of automation technology and robotics, robots are playing an increasingly vital role across various industries. In fields like industrial production, warehouse logistics, and smart homes, precise positioning and obstacle detection are crucial for the efficient operation of robots. Laser measurement sensor, with their high precision, have become key tools for optimizing robot navigation and environmental awareness. In this article, we will explore the role of laser measurement sensors in robot positioning and obstacle detection and how these sensors enhance the intelligence and efficiency of robots.

What is a Laser Measurement Sensor?
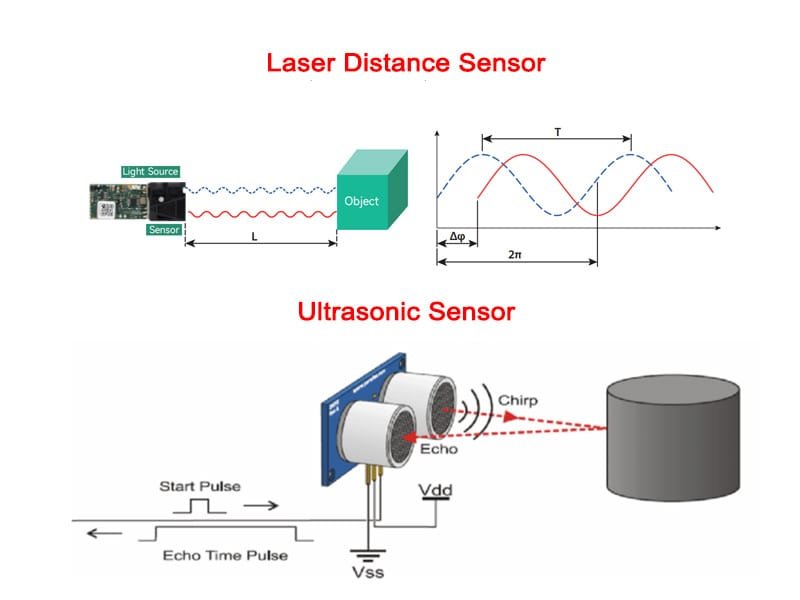
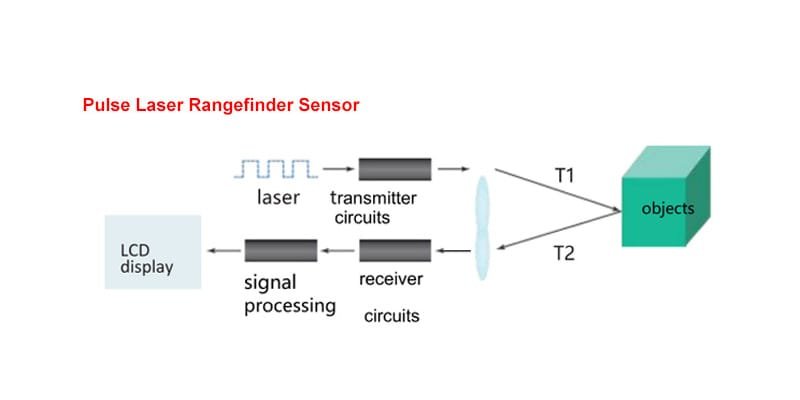
A laser measurement sensor is a device that uses laser technology to perform non-contact distance measurements. By emitting a laser beam and measuring the time it takes for the beam to reflect off a surface, the sensor calculates the distance to the object. Compared to traditional ultrasonic sensors, laser sensors offer higher accuracy and longer measurement ranges, making them widely used in applications requiring precise measurements.
Applications of Laser Measurement Sensors in Robot Positioning
Robot positioning is a crucial aspect of automation systems, especially in dynamic environments. Laser measurement sensors provide highly accurate distance data, helping robots sense their surroundings in real-time for precise positioning. Here are the advantages of using laser distance measure sensor for robot positioning:
1. High Precision Measurement
Laser sensors provide sub-millimeter level accuracy, enabling robots to precisely locate designated positions. In complex production lines or warehouse environments, precise positioning is essential for ensuring robots perform tasks efficiently.
2. Long-Range Measurement
Laser sensors have longer measurement ranges, enabling robots to detect obstacles or targets at greater distances, allowing them to adjust their path in time to avoid collisions.
3. Non-Contact Measurement
Laser sensors do not require physical contact with objects, preventing wear and tear that could occur with traditional contact-based sensors. This makes laser sensors especially reliable in high-speed or complex environments.
Applications of Laser Measurement Sensors in Obstacle Detection
Obstacle detection is a key function in autonomous robot navigation. In dynamic environments, robots must quickly identify and avoid obstacles to ensure safety and efficiency. Laser measurement sensors provide precise distance data, offering crucial environmental awareness for the robot.
1. Real-Time Obstacle Detection
Laser measurement sensors can detect the presence of obstacles in real-time and quickly send feedback to the robot, enabling it to avoid collisions and adjust its path as needed.
2. High-Resolution Data
laser distance measure sensor offer high-resolution distance data, allowing robots to identify small or low obstacles such as cables or parts, even in narrow spaces, ensuring precise operations.
3. Adaptability to Various Environments
Laser sensors work reliably under varying lighting conditions, making them ideal for environments where lighting can change frequently, such as outdoor operations or warehouses with inconsistent lighting.

Integration of Laser Measurement Sensors in Robotic Systems
The advantages of laser measurement sensors make them an essential component in robotic systems. As robotic technology continues to evolve, deep integration of laser sensors with robot control systems and navigation algorithms will further enhance robot autonomy and intelligence.
1. Integration with SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) Algorithms
Laser measurement sensors can be integrated with SLAM algorithms to help robots navigate autonomously in unknown environments. SLAM uses the data from laser sensors to construct environmental maps, calculate the robot’s position in real time, and optimize path planning.
2. Integration with Obstacle Avoidance Algorithms
The data from laser sensors can be combined with robots’ obstacle avoidance algorithms, allowing them to identify and avoid obstacles while navigating. This enables robots to adjust their paths in real time based on laser sensor feedback.
Conclusion
Laser measurement sensors play an indispensable role in robot positioning and obstacle detection, providing precise measurements and enhancing the robot’s ability to perceive its environment. As technology advances, laser measurement sensors will continue to drive the development of robotics, enabling robots to perform smarter and more efficiently across various industries.
To further enhance the accuracy and reliability of robots, adopting high-performance laser measurement sensors will be a key choice in the future of automation. If you’re looking for laser measurement sensors for robotic applications, choose products with high precision, long measurement range, and strong environmental adaptability to boost your robot’s capabilities.