Why Protocol Conversion Matters in Embedded Laser Distance Sensor Systems
Introduction
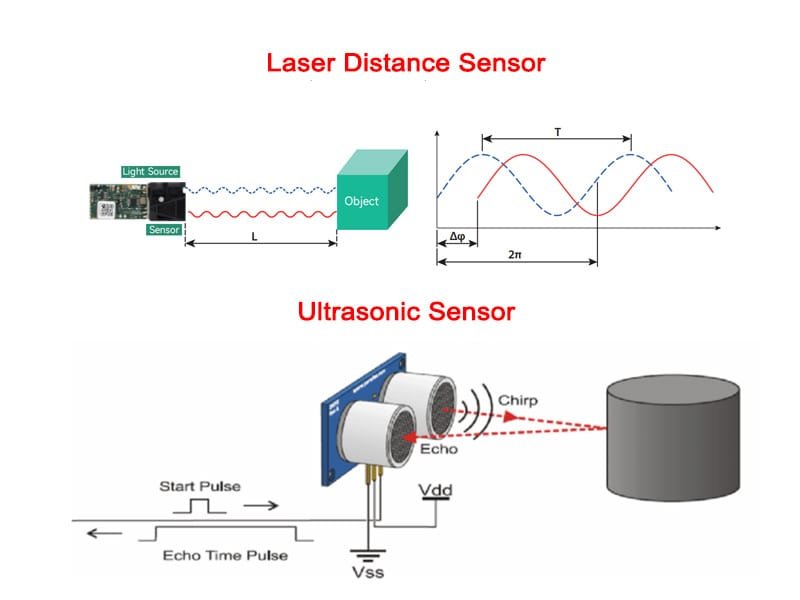
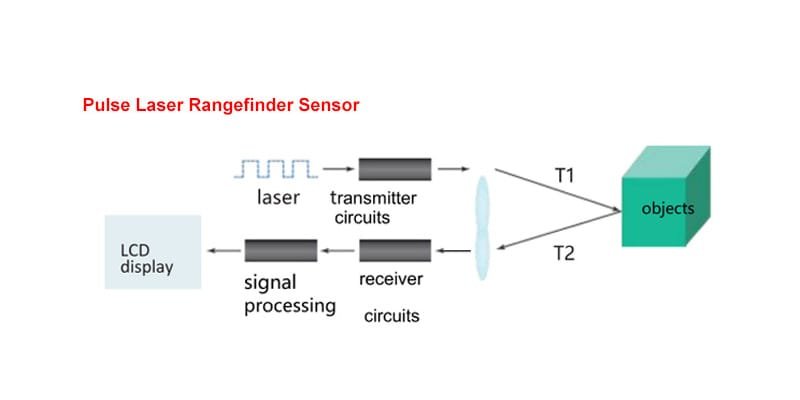
Modern laser distance sensors are smarter than ever, integrating with robotic systems, industrial automation, smart transportation, warehousing, and IoT platforms. While precision optics define measurement accuracy, communication compatibility determines whether a sensor can actually work within complex embedded systems.
However, not all systems use the same communication protocol. Some controllers support UART only, others require CAN bus, and many industrial PLCs depend on RS485. This mismatch creates a vital need for protocol conversion.

In environments where reliability and real-time responsiveness matter, proper protocol conversion ensures stable data exchange — unlocking full system functionality and maximizing performance of laser distance measurement modules.
Why Protocol Conversion Is Needed
MCU resources are limited. A single microcontroller may not support every communication protocol required in a system. As sensor networks scale or equipment upgrades occur, there is often a need to:
- Expand communication channels
- Upgrade legacy systems to modern communication standards
- Adapt different devices to a universal platform
- Improve anti-interference capabilities
- Increase communication distance or transfer rate
This is where protocol converters play a key role. They bridge communication layers, enabling laser distance sensors and controllers to speak the same language.
For example:
If a PLC requires RS485/Modbus, but the sensor only supports UART → A UART to RS485 converter must be used.
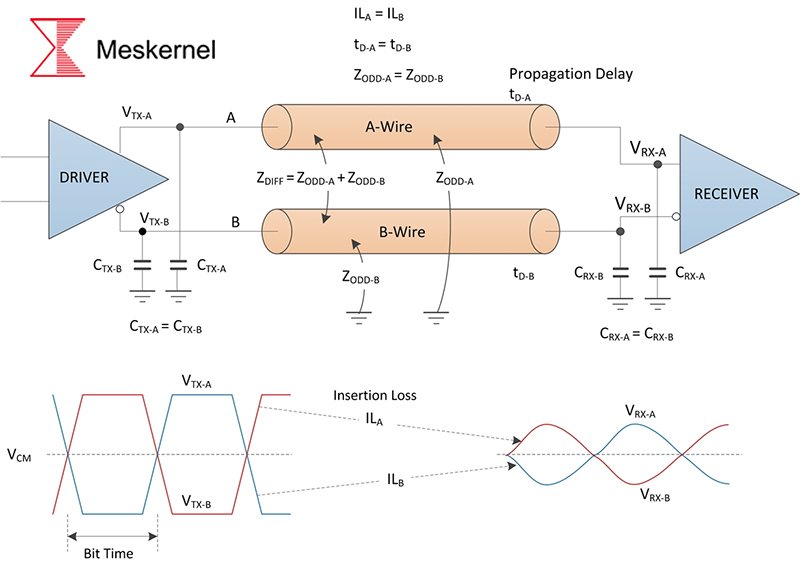
Common Protocol Conversion Scenarios
Laser distance sensor applications frequently require conversion between:
| From | To | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| UART | RS485 | Long-distance industrial communication |
| SPI | UART | Microcontroller expansion |
| I2C | UART | Multi-sensor networking |
| USB | UART | PC debugging and configuration |
| CAN | UART | Automotive or robotics applications |
Meskernel products such as LDL-T and LDL-S support UART and RS485 natively, while converters can extend interface options to CAN, I2C, and USB for broader compatibility.
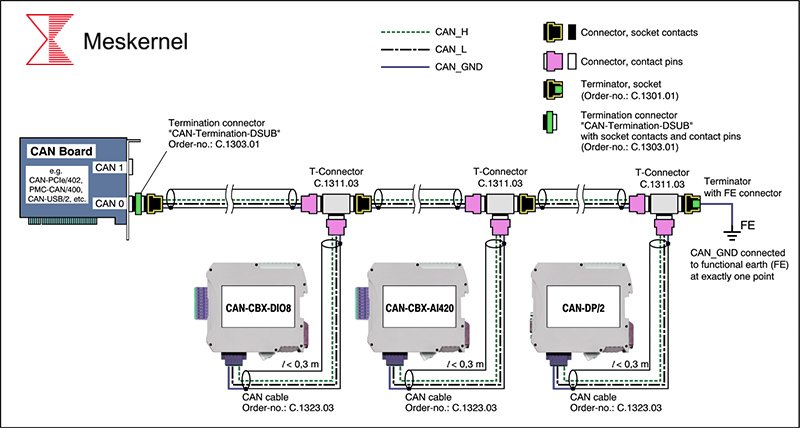
Case Study: Industrial Automation with RS485 Conversion
In large factory automation:
- Sensors may be tens or hundreds of meters away from the control cabinet
- Strong electromagnetic noise affects data transmission
- Multiple laser sensors may operate simultaneously in a network
RS485 communication solves these issues due to:
Anti-interference differential signaling
Up to 1000m transmission distance
Support for multi-node bus topology
By converting UART output from a laser distance sensor to RS485, engineers ensure reliable data synchronization even under harsh electrical environments.
Case Study: SPI / I2C to UART in Embedded Development
Embedded developers often require:
- Multiple UART interfaces while the MCU has only one
- Fast communication between sensor clusters
- Compact wiring for PCB space savings
Solutions include:
I2C to UART expansion chips
→ Example: Adding multiple UART channels for numerous laser sensors
SPI to UART converters
→ High-speed controller sends commands while UART interacts with sensors
These conversions enable multi-sensor fusion systems such as:
- AGV / AMR navigation
- Robotic arm position sensing
- 3D measurement scanning systems
Protocol Conversion Increases System Flexibility
The true value lies in adaptability.
With proper protocol conversion, laser distance sensors can be upgraded or replaced without redesigning the entire system. Engineers gain:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Device compatibility | Easier integration into legacy or advanced systems |
| Scalability | Add more sensors seamlessly |
| Reduced wiring complexity | Lower maintenance cost |
| Improved signal reliability | Higher measurement stability |
| Better lifecycle upgrade support | Long-term investment protection |
Meskernel focuses on designing flexible signal interfaces to help users adapt to multi-protocol systems quickly.
Real-World Applications
Protocol conversion can be found in many industries:
- Smart Warehousing: CAN conversion enhances automated forklift control
- Robotics: SPI to UART conversion enables rapid sensor data fusion
- Traffic & Safety: RS485 laser distance sensors monitor vehicle flow
- Agricultural Machinery: CAN ensures reliable communication on long vehicles
- Security & Surveillance: USB connection for PC visualization and data logging
Whether used for mapping, collision avoidance, or precision measurement, the right communication bridge ensures the entire sensing network functions flawlessly.
Future Trends: Toward Universal and Intelligent Interfaces
As communication technologies evolve, embedded systems are moving toward:
Auto-recognition of protocols
Hybrid combination of wired + wireless (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi)
Ethernet-based laser distance sensor networks
Smart configurable interfaces via software commands
Future laser measurement devices will feature dynamic protocol switching, giving engineers ultimate flexibility to configure their systems without hardware changes.
Meskernel is actively developing next-generation intelligence communication modules, ensuring that its laser distance sensors always remain compatible with future automation standards.
Conclusion
Protocol conversion is not merely a technical supplement — it is a critical enabler that determines whether a laser distance sensor can seamlessly integrate into industrial and embedded systems.
With proper converter selection and interface configuration, engineers unlock:
Stable long-distance data transmission
Full compatibility with multiple controllers
High-speed synchronized measurement
Scalable and future-proof automation networks
In a rapidly evolving technology landscape, the ability to adapt communication protocols ensures that laser distance sensors can continue to deliver precision, efficiency, and intelligence across every application.