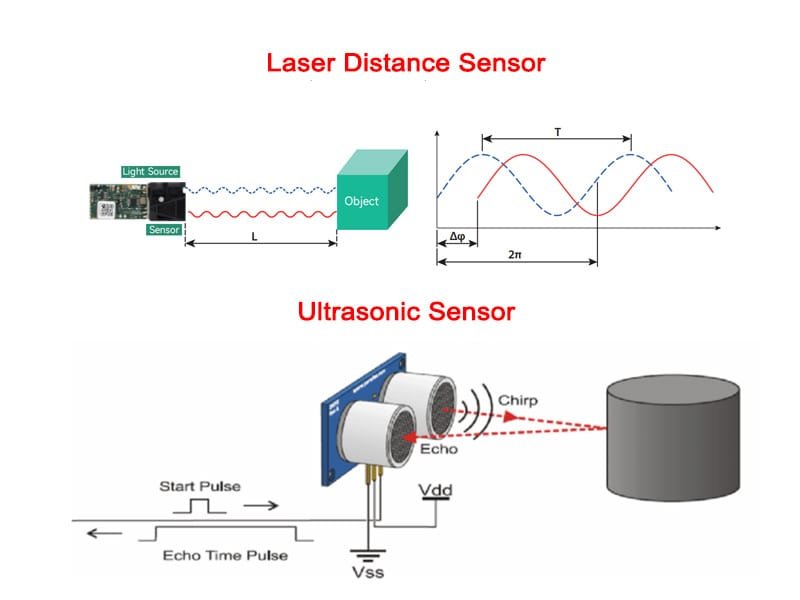
Roter oder grüner Laser-Distanzsensor: Leistungsvergleich und Auswahlhilfe
Einführung
Lasersensoren spielen eine entscheidende Rolle in der modernen industriellen Automatisierung, Robotik, Logistik und Präzisionssteuerung. Unter verschiedenen optischen Lösungen ist die Wahl zwischen einem Grüner Laser-Sensor und eine rote Laser-Alternative ist eine häufige Herausforderung für Ingenieure und Systemintegratoren.
Beide Optionen gehören zwar zu den Lasersensoren für die Entfernungsmessung, aber ihre optischen Wellenlängeneigenschaften führen zu erheblichen Unterschieden in Bezug auf Sichtbarkeit, Genauigkeit und Umweltverträglichkeit. Die Wahl des falschen Lasersensors kann zu instabilen Messwerten, Ausrichtungsschwierigkeiten oder geringerer Messeffizienz führen.
Dieser Artikel bietet einen detaillierten Leistungsvergleich zwischen grüner und roter Lasertechnologie und hilft Ihnen zu verstehen, wie ein grüner Lasersensor in realen Anwendungen funktioniert und wie Sie den richtigen Lasersensor für die Abstandsmessung auswählen.
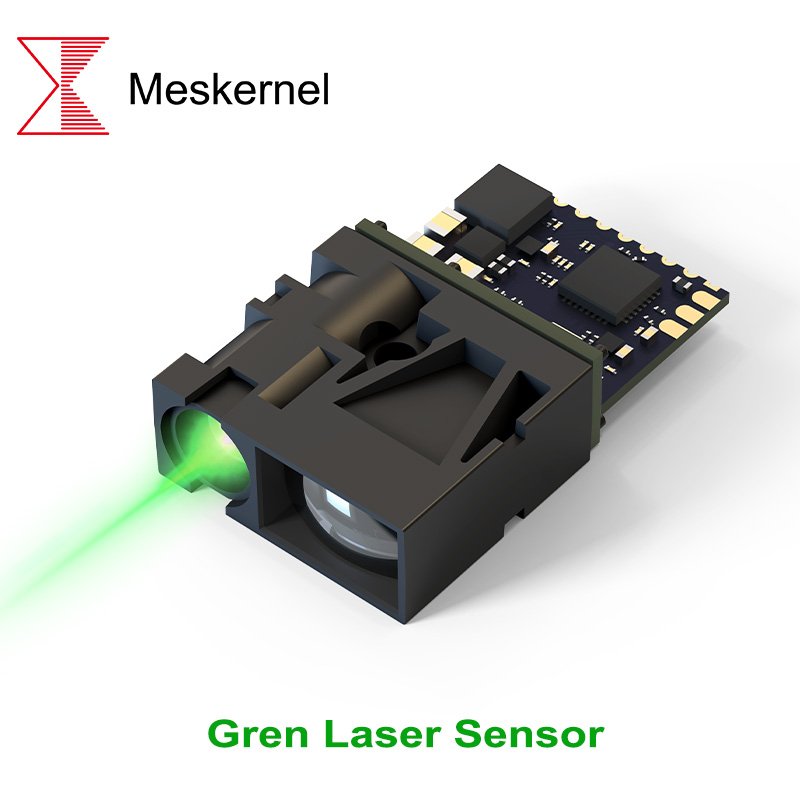
Was ist ein grüner Lasersensor?
A Grüner Laser-Messsensor verwendet einen sichtbaren grünen Laserstrahl, der typischerweise im Wellenlängenbereich von 510-550 nm arbeitet, um eine Entfernungsmessung nach dem Phasenverschiebungs- oder Lichtlaufzeitprinzip durchzuführen. Aufgrund der hohen Empfindlichkeit des menschlichen Auges für grünes Licht bieten grüne Lasersensoren im Vergleich zu roten Laserlösungen eine bessere Sichtbarkeit des Strahls.
Aufgrund dieser hohen Sichtbarkeit eignet sich ein grüner Lasersensor besonders für Anwendungen, bei denen eine manuelle Ausrichtung, eine visuelle Bestätigung oder eine präzise Positionierung erforderlich ist. Darüber hinaus bietet die grüne Lasertechnologie oft eine stabilere Leistung auf schwierigen Oberflächen wie dunklen, reflektierenden oder kontrastarmen Materialien.
Aufgrund dieser Vorteile werden grüne Lasersensoren zunehmend in hochpräzisen industriellen Mess- und fortschrittlichen Automatisierungssystemen eingesetzt.
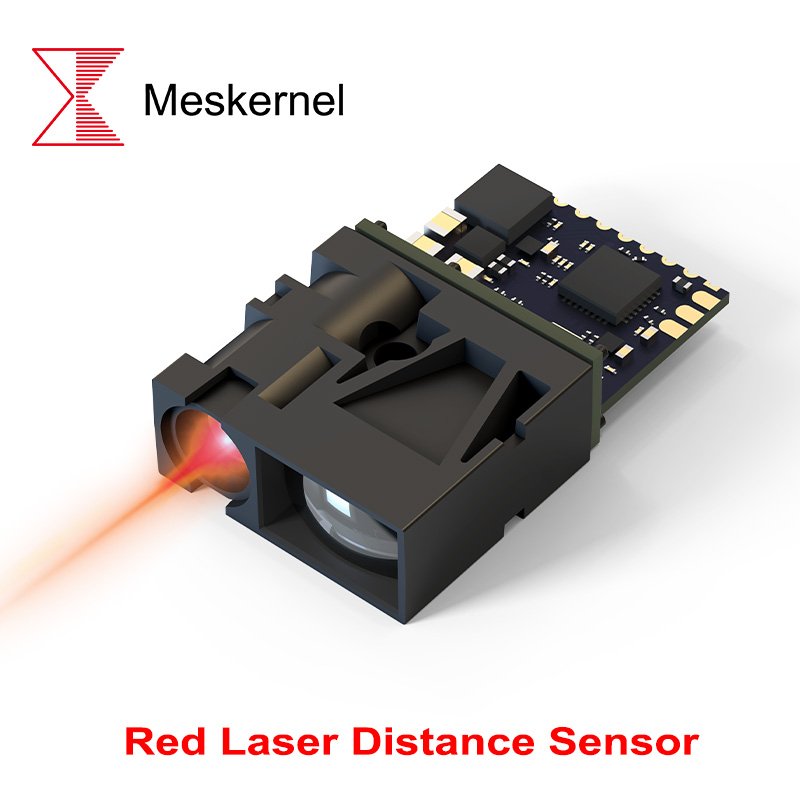
Rote Laser-Distanzsensoren verstehen
Rote Lasersensoren arbeiten in der Regel im Wellenlängenbereich von 610-690 nm und gehören zu den am weitesten verbreiteten Lasersensoren für die Abstandsmessung. Ihr langjähriger Einsatz in industriellen Umgebungen macht sie zuverlässig, kostengünstig und einfach zu integrieren.
Rote Laser-Distanzsensoren funktionieren gut unter stabilen Innenraumbedingungen und werden häufig in der Lagerautomatisierung, in Logistiksystemen und bei industriellen Standard-Positionierungsaufgaben eingesetzt. Ihre Sichtbarkeit kann jedoch bei starkem Umgebungslicht oder bei der Messung dunkler Oberflächen eingeschränkt sein.
Bei Anwendungen, die keine visuelle Ausrichtung erfordern, sind rote Lasersensoren nach wie vor eine praktische und wirtschaftliche Option.
Sichtbarkeit und Ausrichtungsleistung
Die Sichtbarkeit ist einer der wichtigsten Leistungsunterschiede zwischen einer Grüner Laser und eine rote Laserlösung.
Grüne Laserstrahlen sind für das menschliche Auge deutlich besser sichtbar als rote Laserstrahlen bei gleicher Leistung. Dieser Vorteil vereinfacht die Installation, Kalibrierung und Wartung, insbesondere in hellen industriellen Umgebungen.
Für Systeme, die eine häufige manuelle Einrichtung oder eine visuelle Verfolgung in Echtzeit erfordern, bietet ein grüner Lasersensor klare betriebliche Vorteile. Im Gegensatz dazu benötigen rote Lasersensoren unter ähnlichen Bedingungen möglicherweise zusätzliche Ausrichtungswerkzeuge.
Genauigkeit und Oberflächenkompatibilität
Bei der Auswahl von Lasersensoren für die Abstandsmessung sind Genauigkeit und Oberflächenanpassung entscheidend.
A Grüner Laser-Sensor bietet in der Regel eine verbesserte Signalstabilität:
- Dunkle oder schwarze Oberflächen
- Glänzende oder metallische Ziele
- Materialien mit geringem Reflexionsvermögen
Diese Eigenschaften reduzieren das Messrauschen und verbessern die Wiederholbarkeit in anspruchsvollen Umgebungen.
Rote Laser-Distanzsensoren liefern zuverlässige Genauigkeit auf hellen, matten oder gleichmäßigen Oberflächen, können aber bei schwierigen Zielen eine geringere Signalstärke aufweisen. Für Anwendungen mit unterschiedlichen Materialien bietet die grüne Lasertechnologie mehr Flexibilität.
Anpassungsfähigkeit an die Umwelt
Umgebungsbedingungen wie Beleuchtung, Hintergrundkomplexität und Arbeitsabstand wirken sich direkt auf die Leistung des Lasersensors aus.
A Grüner Laser-Sensor zeigt eine bessere Anpassungsfähigkeit in:
- Umgebungen mit viel Umgebungslicht
- Außen- oder Halbaußenanwendungen
- Komplexe industrielle Hintergründe
Daher eignen sich grüne Lasersensoren gut für die intelligente Landwirtschaft, automatische Inspektionen und Roboterführungssysteme.
Rote Lasersensoren funktionieren optimal in kontrollierten Innenräumen, in denen die Licht- und Hintergrundbedingungen stabil bleiben.
Stromverbrauch und Kostenüberlegungen
Bei der Bewertung von Lasersensoren sind die Systemkosten und die Leistungseffizienz wichtige Entscheidungsfaktoren.
Rote Lasersensoren sind aufgrund ausgereifter Herstellungsverfahren und ihrer weiten Verbreitung in der Regel kostengünstiger. Sie eignen sich für große Installationen, bei denen die Kosteneffizienz entscheidend ist.
A Grüner Laser haben zwar etwas höhere Anschaffungskosten, aber die bessere Sichtbarkeit und Messstabilität rechtfertigen oft die Investition in hochpräzise oder komplexe Anwendungen.
Wie man den richtigen Lasersensor auswählt
Bei der Auswahl des am besten geeigneten Lasersensors für die Entfernungsmessung sind die folgenden Kriterien zu berücksichtigen:
- Anforderungen an die Sichtbarkeit
Wählen Sie einen grünen Lasersensor, wenn eine visuelle Ausrichtung oder ein Eingriff des Bedieners erforderlich ist. - Zieloberfläche Typ
Grüne Lasersensoren funktionieren besser auf dunklen oder reflektierenden Oberflächen. - Betriebsumgebung
Im Freien oder in Umgebungen mit starkem Licht wird die grüne Lasertechnologie bevorzugt. - Haushaltszwänge
Rote Lasersensoren sind ideal für kostensensitive Standardanwendungen.
Wenn Sie diese Faktoren mit Ihren Systemanforderungen abgleichen, können Sie die effektivste Lösung unter den verfügbaren Lasersensoren auswählen.
Häufige Anwendungsszenarien
Grüner Laser-Sensor Anwendungen
- Industrielle Präzisionsmessung
- Positionierung und Navigation von Robotern
- Intelligente Landwirtschaft - Sensorik
- Hochpräzise Objekterkennung
Lasersensoren für die Abstandsmessung (allgemein)
- Automatisierung von Fabriken
- Logistik und Lagerhaltung
- Eingebettete Messsysteme
- Industrielle Überwachung
Die grüne Lasertechnologie erweitert den Anwendungsbereich moderner Lasersensoren.
Schlussfolgerung
Die Wahl zwischen einer Grüner Laser-Sensor und einem roten Laser-Distanzsensor hängt von anwendungsspezifischen Anforderungen und nicht von einer einzigen Leistungskennzahl ab. Grüne Lasersensoren bieten eine bessere Sichtbarkeit, eine bessere Anpassungsfähigkeit an Oberflächen und eine höhere Leistung in schwierigen Umgebungen.
Wenn Ingenieure und Integratoren diese Unterschiede verstehen, können sie sicher sein Auswahl des richtigen Lasersensors für die Entfernungsmessung, Dadurch werden eine stabile Leistung, genaue Ergebnisse und eine langfristige Zuverlässigkeit des Systems gewährleistet.