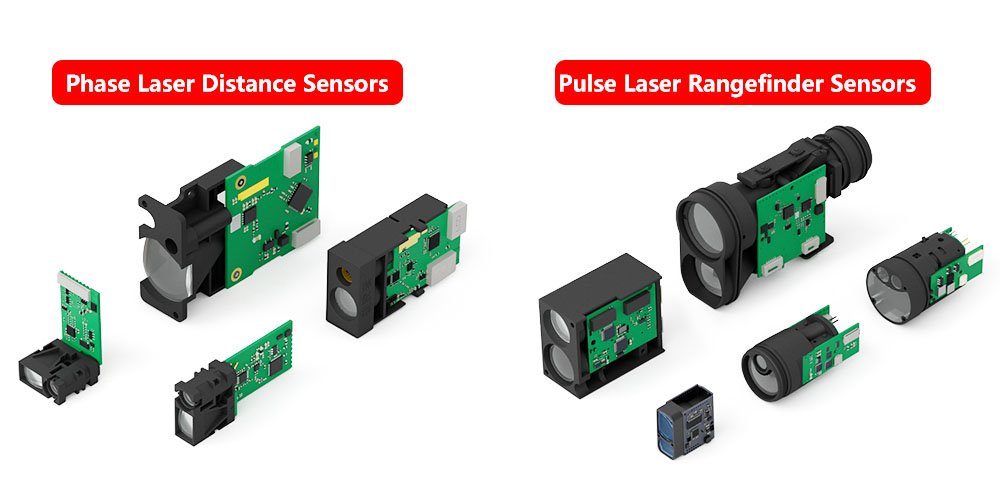
How to Measure Distance with a Laser Sensor?
Introduction How to Measure Distance with a Laser Sensor: Laser sensors have become a popular tool for accurately measuring distances in various industries, from construction to manufacturing. Their precision, speed, and ease of use make them an ideal choice for professionals and hobbyists alike. But how exactly do you measure distance with a laser sensor? In this article, we’ll walk through the process step-by-step, explain the underlying principles, and provide tips on getting the most accurate measurements.

Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring Distance with a Laser Sensor
Set Up the Laser Sensor
Begin by placing the laser sensor on a stable surface or hold it steadily if it’s a handheld device. Ensure that the sensor is aligned with the target you’re measuring. The sensor emits a laser beam in a straight line, so the device must be aimed directly at the object for an accurate reading.
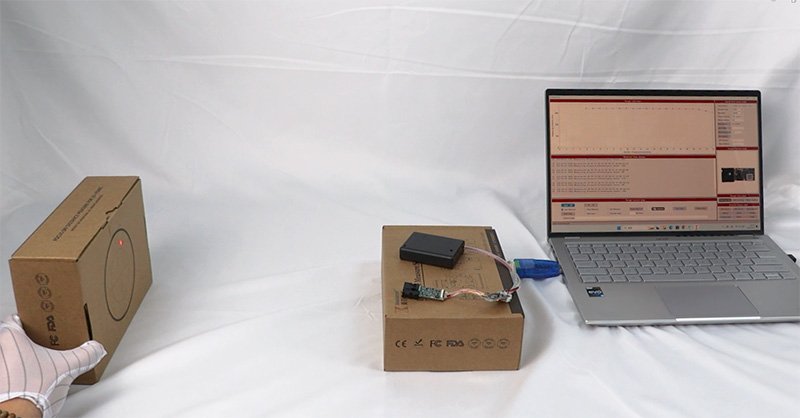

Activate the Laser
Turn on the laser sensor, and depending on the model, press the button to emit the laser beam. The device will send a pulse of light (a laser) toward the target. Some sensors may have options to adjust the laser beam’s focus or range, depending on the distance you need to measure.
Measure the Return Time
Once the laser hits the object, it will bounce back to the sensor. The device calculates the time it took for the light to travel to the target and return (known as the time-of-flight). With the speed of light being constant, the sensor can use this time to calculate the exact distance between the sensor and the target.
Read the Display
The sensor’s onboard processor will quickly calculate the distance and display the result on the screen. This reading will typically be shown in metric (meters or centimeters) or imperial (feet or inches) units, depending on your settings. Many modern laser sensors have a digital display for easy reading.

Fine-Tuning for Accuracy
For optimal accuracy, ensure:
Clear Line of Sight: There should be no obstructions between the sensor and the target.
Surface Consideration: Some surfaces (e.g., glossy or transparent) may cause laser reflection issues. Use a matte or rough surface for better accuracy, or place a reflective target on the object if necessary.
Stable Positioning: To avoid errors caused by movement, especially for long-distance measurements, use a tripod or place the sensor on a stable platform.
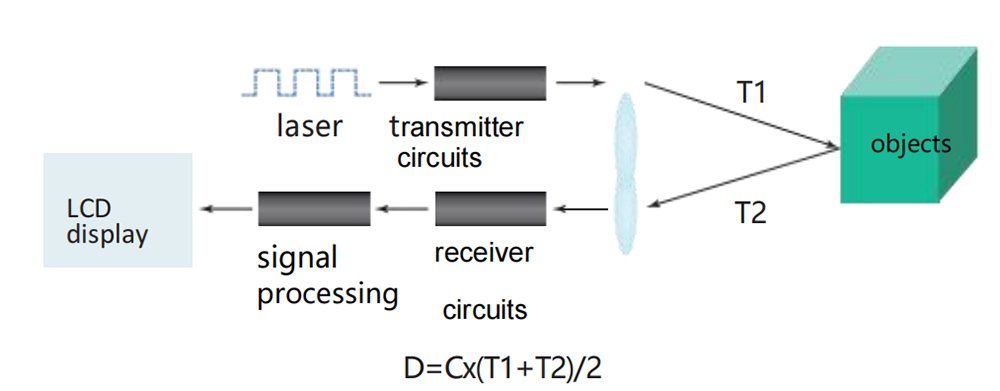
How Does a Laser Sensor Calculate Distance?
Laser distance sensors use the time-of-flight (ToF) method to calculate distances. Here’s a simple breakdown:
Emit a Laser Beam: The sensor sends out a narrow, focused laser beam toward the target.
Reflection: The laser hits the target and reflects back to the sensor.
Time Measurement: The time it takes for the light to travel to the object and return is recorded.
Distance Calculation: Using the formula
Distance=Speed of Light×Time/2, the sensor calculates the distance.
Since the speed of light is constant, the sensor can calculate the distance by measuring the time it takes for the laser to bounce back. This principle ensures high accuracy, often down to millimeters.
Applications of Laser Distance Sensors
Laser sensors are widely used in many fields:
Construction: Laser sensors are invaluable for measuring room dimensions, layout designs, and outdoor distances quickly and precisely.
Manufacturing: In production lines, they ensure components meet precise specifications, playing a vital role in quality control (internal link).
Robotics: Used for navigation and obstacle detection, laser sensors help robots sense their environment.
Surveying: In land surveys, laser sensors allow for accurate long-distance measurements without physical contact.
Why Choose a Laser Sensor for Distance Measurement?
High Accuracy: Laser sensors provide measurements with millimeter precision, making them ideal for tasks where exact distance is critical.
Speed: The process is nearly instantaneous, allowing for rapid measurements in fast-paced environments.
Non-Contact Measurement: The ability to measure without touching the object is perfect for inaccessible or hazardous areas.
Long Range: Laser sensors can measure from just a few centimeters to several hundred meters.
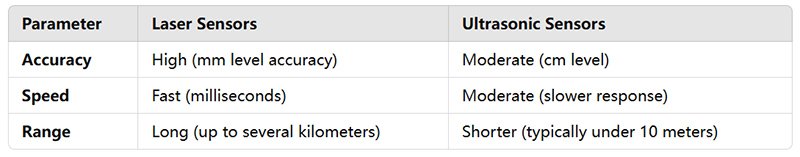
Tips for Getting the Best Results with Laser Distance Sensors
Use Reflective Targets: If measuring on glossy or transparent surfaces, use reflective tape or a flat, matte object to get more reliable results.
Avoid Dust or Smoke: Environmental factors like dust or fog can interfere with the laser beam, so clear the path if possible.
Use a Tripod for Long Distances: For distances beyond 50 meters, securing the sensor on a tripod will help reduce movement and improve accuracy.
Conclusion:
Measuring distance with a laser sensor is a simple yet powerful method that offers high precision and efficiency. By understanding how the time-of-flight principle works and following best practices for setup, you can ensure accurate measurements in a wide variety of applications. Whether you’re a professional in construction, manufacturing, or robotics, a laser distance sensor is an invaluable tool for your work.